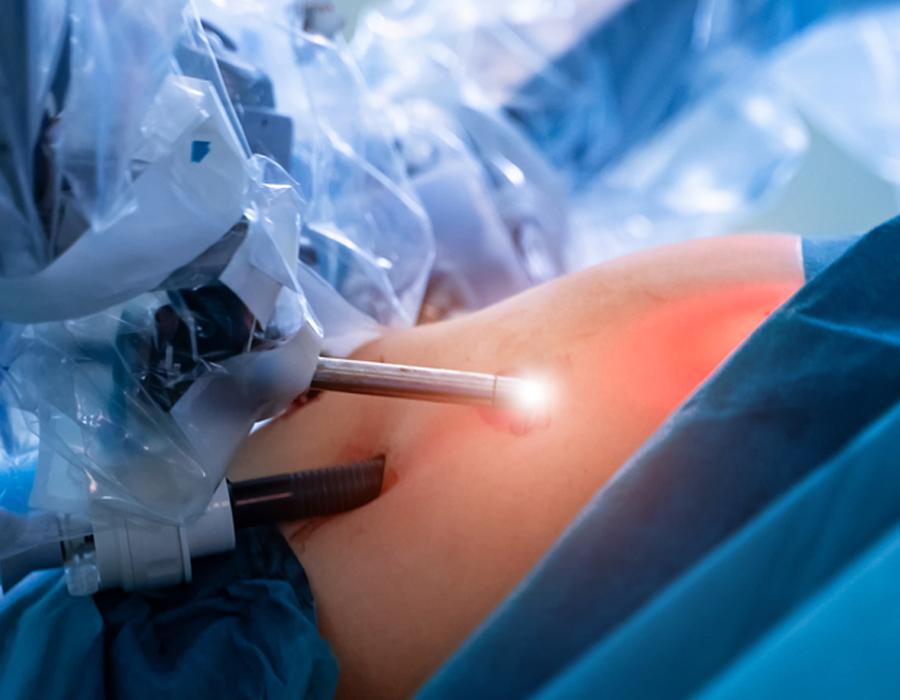
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, is a minimally invasive surgical technique that utilizes robotic systems to assist surgeons in performing complex procedures with enhanced precision, flexibility, and control. It combines advanced technology with the skills of the surgeon to provide a range of potential benefits for patients. Here are some key points about robotic surgery:
- Robotic System: Robotic surgery systems typically consist of a console where the surgeon sits and controls the instruments, robotic arms that hold and manipulate the surgical instruments, and a high-definition 3D camera that provides a magnified and detailed view of the surgical site.
- Minimally Invasive Approach: Robotic surgery is usually performed using small incisions, similar to traditional laparoscopic surgery. The surgeon controls the robotic arms from the console, which translates their hand movements into precise movements of the instruments inside the patient's body.
- Enhanced Precision and Dexterity: The robotic system offers increased precision, dexterity, and range of motion compared to traditional laparoscopic instruments. The robotic arms can mimic the movements of the surgeon's hands with enhanced stability and flexibility, allowing for delicate and precise maneuvers.
- Improved Visualization: The 3D high-definition camera provides a magnified and detailed view of the surgical site, allowing the surgeon to see structures more clearly and in greater detail. This enhanced visualization can be particularly beneficial for complex and intricate procedures.
- Benefits for Surgeons: Robotic surgery provides ergonomic advantages for surgeons. The console is designed to offer a comfortable seated position, reducing fatigue during long procedures. The surgeon has a more intuitive control of the instruments, enabling improved surgical performance.
- Potential Patient Benefits: Robotic surgery has the potential to offer several benefits for patients, including reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, smaller incisions resulting in less scarring, less postoperative pain, faster recovery, and a quicker return to normal activities compared to traditional open surgery.
- Procedure Availability: Robotic surgery is used in various surgical specialties, including urology, gynecology, general surgery, thoracic surgery, colorectal surgery, and more. Common procedures performed using robotic surgery include prostatectomy, hysterectomy, colorectal surgery, and lung surgery.
- Surgeon Training and Expertise: Performing robotic surgery requires specialized training and expertise. Surgeons undergo training programs and certification processes to become proficient in using the robotic system and performing robotic-assisted procedures.