Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS), also known as minimally invasive techniques or laparoscopic surgery, is a surgical approach that aims to minimize the size of incisions and reduce trauma to the body compared to traditional open surgery. It involves the use of specialized instruments and advanced technologies to perform surgical procedures through small incisions.
Robotic Surgery
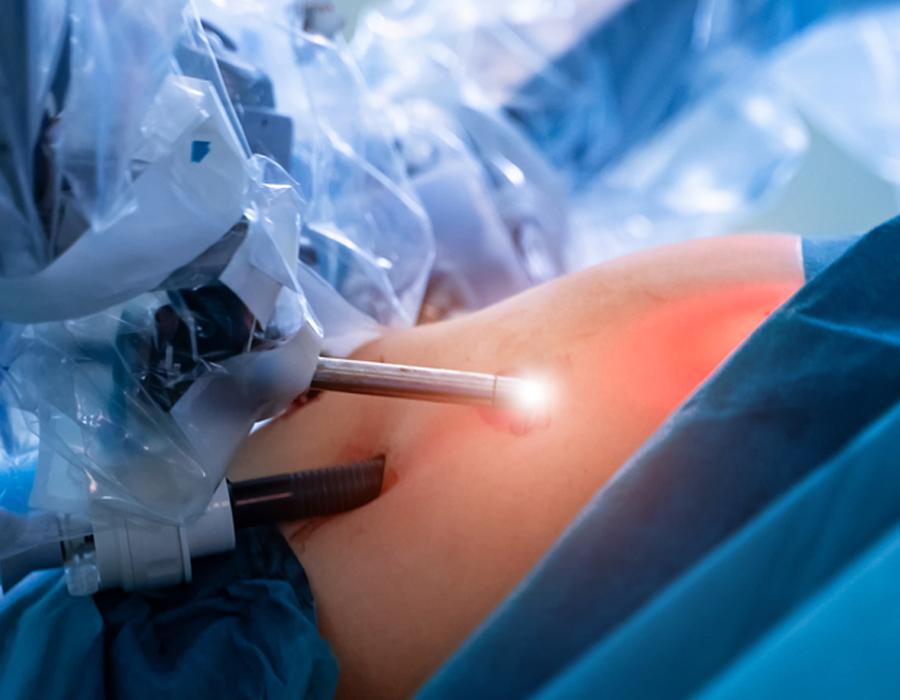
Robotic minimally invasive surgery, also known as robotic-assisted surgery, is an advanced surgical technique that combines the precision and dexterity of robotic systems with the benefits of minimally invasive surgery. It allows surgeons to perform complex procedures with enhanced precision, control, and visualization.
- Robotic surgical system: Robotic surgery systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, are commonly used in robotic-assisted surgery. These systems consist of robotic arms controlled by the surgeon, a high-definition 3D camera, and specialized instruments. The surgeon operates the robotic arms from a console near the patient, controlling the movements with hand and foot controls.
- Minimally invasive approach: Robotic surgery is performed through small incisions, similar to traditional laparoscopic surgery. However, robotic systems provide greater maneuverability and more flexible instruments compared to traditional laparoscopic tools. This enables surgeons to access and operate in hard-to-reach areas with improved precision and control.
Robotic minimally invasive surgery represents a significant advancement in surgical techniques, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater precision and patient benefits. However, it's important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate surgical approach for your specific condition.
Laparoscopic Surgery
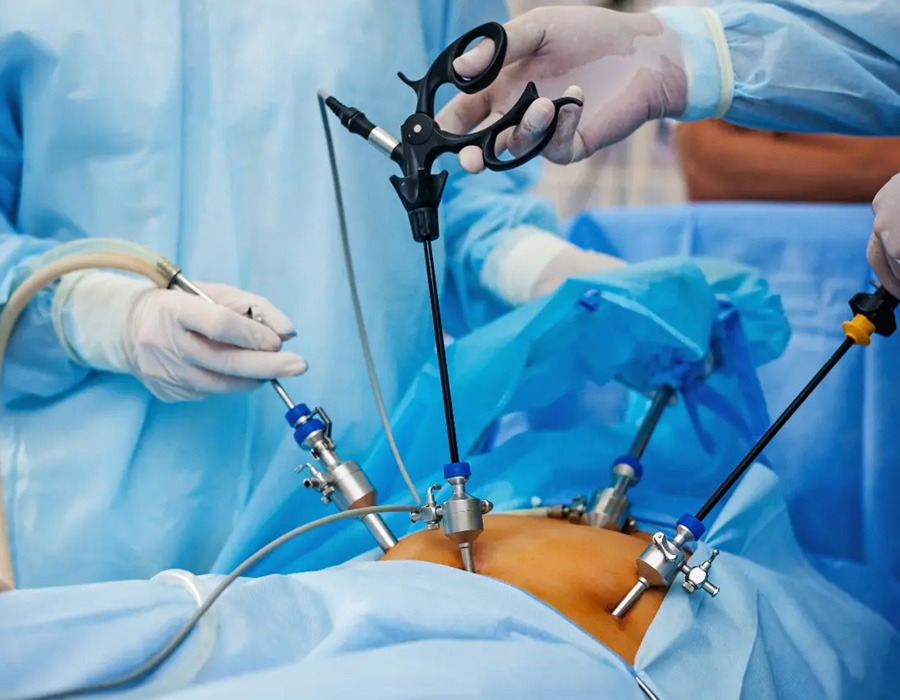
Laparoscopic minimally invasive surgery, also known as laparoscopy, is a surgical technique that uses small incisions and specialized instruments to perform procedures inside the abdomen or pelvis. It offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, reduced postoperative pain, faster recovery, and improved cosmetic outcomes.
- Procedure overview: During laparoscopic surgery, a laparoscope—a thin, lighted tube with a camera—is inserted through a small incision, allowing the surgeon to visualize the surgical site on a monitor. Additional small incisions are made to introduce specialized instruments that the surgeon uses to perform the procedure. The surgeon manipulates these instruments from outside the body, guided by the images provided by the laparoscope.
- Small incisions: The incisions made in laparoscopic surgery are typically around 0.5 to 1.5 centimeters in length, significantly smaller than the larger incisions required in open surgery. These smaller incisions result in less tissue trauma, reduced blood loss, and minimal scarring.
- Reduced postoperative pain: Laparoscopic surgery is associated with less postoperative pain compared to open surgery. The smaller incisions and reduced tissue trauma contribute to a faster recovery and decreased reliance on pain medication.

